June 2023
Why is HbA1c more convincing regarding good or bad blood sugar control?
HbA1c is a "powerhouse" of a diagnostic test, according to the American Diabetes Association.
What is the HbA1c test?
The HbA1c blood test measures how much blood sugar is attached to your hemoglobin. A1C stands for glycated hemoglobin. Glycated hemoglobin describes how your red blood cells (containing a protein called hemoglobin) become loaded with sugar. As sugar circulates in your bloodstream (such as after eating), it sticks to the hemoglobin in your red blood cells. Sugar is sticky, and in your body, it stays attached to your hemoglobin for up to 3 months (the average lifespan of your red blood cells).
The more sugar in your bloodstream, the more red blood cells are covered with sugar molecules. The HbA1c test measures the percentage of the hemoglobin in your red blood cells covered in sugar. So the higher your average blood sugar level for the past three months, the higher the number of "sugary" red blood cells, and the higher your HbA1c test result.
What are normal HbA1c ranges?
The A1C test is like a baseball player's season average for you sports statheads — it tells you about a player's overall success. However, your A1C does not mean you know about your blood sugar for just one day, just like a player's single-game batting record won't tell you if they are a good player. For adults, healthcare providers use the following HbA1c target ranges[1]:
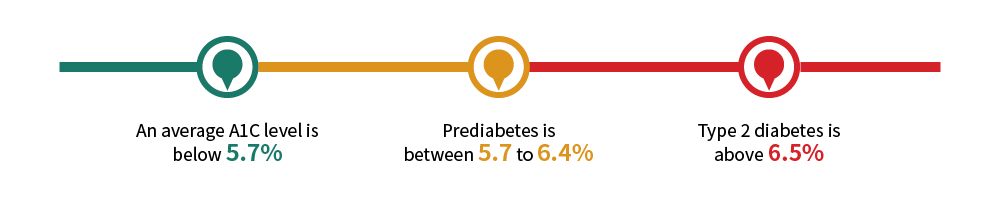
The goal for most adults with diabetes is an A1C that is less than 7%. But, just as a younger, stronger baseball player may have a better season average than an 80-year-old grandfather with poor eyesight, HbA1cs vary significantly with age.
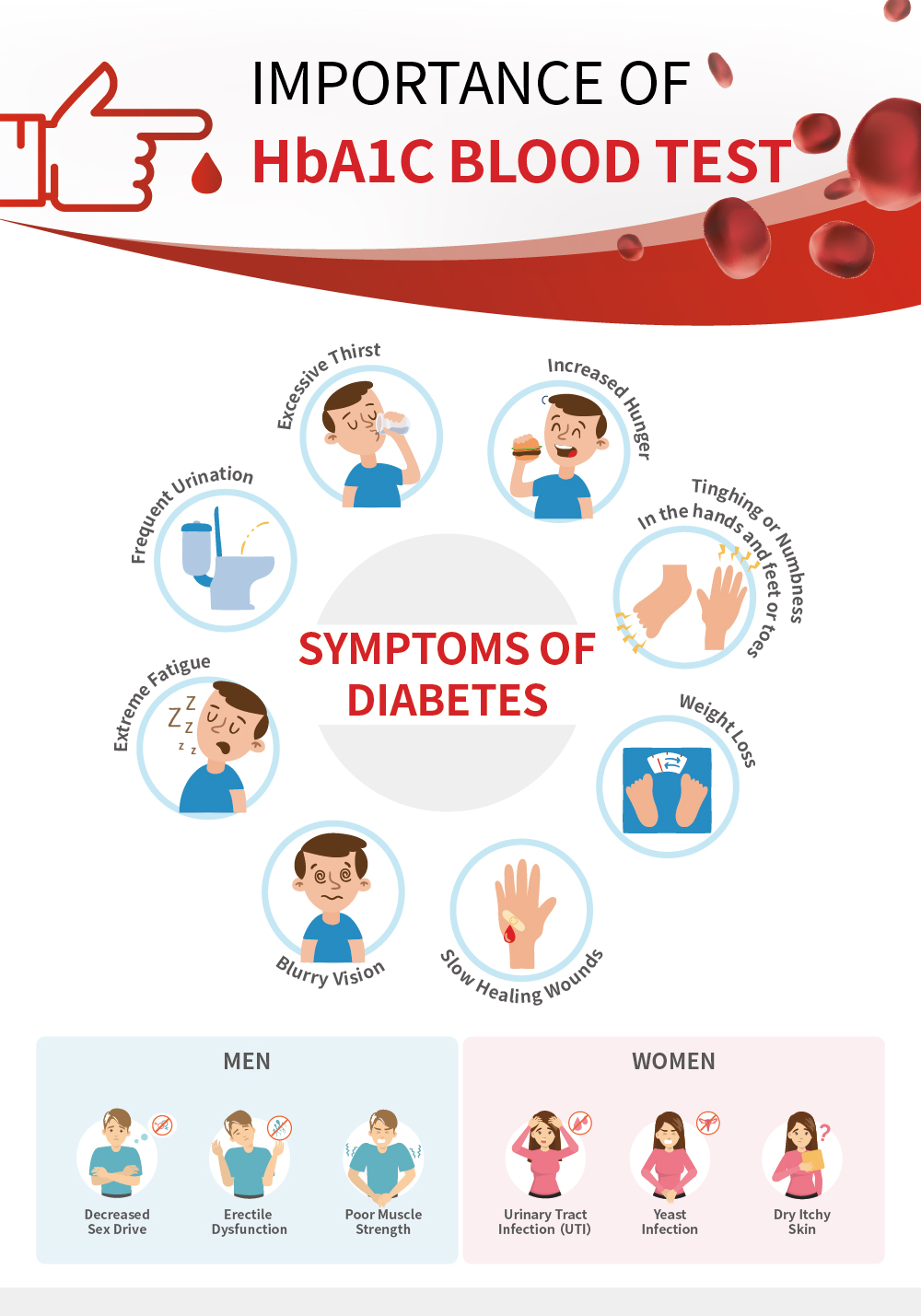
At what conditions should you check your HbA1C?
The CDC recommends getting a baseline A1C test if you're an adult over age 45 or are under 45, are overweight, and have one or more risk factors for prediabetes or type 2 diabetes[2]. You are at risk for diabetes if you[2]:
How to lower your HbA1c levels
If your levels have exceeded your target since your last check, it's understandable to worry. Even a slightly high HbA1c level puts you at risk of developing severe complications in your body. But knowing your numbers and what that means is an essential and good first step – now you need to know how to lower them.
Lots of things can cause your HbA1c levels to change, and there are actions you and your healthcare team can take to bring them down to your target level:
And remember, get advice from your healthcare team. They're here to help.

Getein's Care with HbA1c
As one of the leading in vitro diagnostic companies in China, Getein has always had the health and well-being of all humans at heart and has developed a complete solution for diabetes, a problem where all humans may be at risk together.
First of all is Getein's most trusted POCT solution, in terms of technology we even use a patented lyophilized microsphere process to ensure the adequacy of the reaction. Not only that, Getein has also introduced the MAGICL 6000, a compact and innovative chemiluminescent solution that can accurately detect your HbA1c and help you monitor your diabetes problem more accurately.
Reference:
[1] A1C. MedlinePlus. URL. Updated December 22, 2015. Accessed December 22, 2022.
[2] Diabetes Risk Factors. CDC. URL. Updated April 5, 2022. Accessed December 22, 2022.

Open WeChat and Scan the QR Code. Stay Tuned with Us.